Writing a good assignment starts with understanding how to form the basic structure. The first hint comes from the learning objectives. If you’re given clear learning objectives, you should address each of those within your submission.
Table of contents
Disclaimer: Do not copy and paste anything in the blog post since it is already published online and some are generated using ChatGPT 5.2 Pro and Gemini 3.
In order to address each elements of a good assignment submission, I have taken the first assignment of Basic Epidemiology module as an example.
A cohort study was conducted to assess the relationship between alcohol use and oesophageal cancer over a 20-year follow-up period. The study included 2,000 individuals, of whom 800 were alcohol users and 1,200 were non-alcohol users. At the end of the study, 160 alcohol users and 40 non-alcohol users developed oesophageal cancer.
- 1.1 Construct a 2×2 table summarising the data.
- 1.2 Calculate and interpret the following effect measures:
- 1.2.1 Incidence of oesophageal cancer in each group
- 1.2.2 Relative Risk (RR)
- 1.2.3 Attributable Risk (AR)
- 1.2.4 Attributable Risk Percent (ARP)
- 1.3 Briefly discuss confounding and how it could influence the results of this study.
In the first glance, module lecturer hasn’t given any additional information related to learning objectives or learning outcomes, marking criteria or even word count. Therefore, you could address it with your own structure.
First, it is a good rule of thumb to start with widely used definitions. This assignment is related to cohort study in epidemiology. Then, we are talking about exposure and outcome 2×2 table. Next important keywords are Relative Risk (RR), Attributable Risk (AR) and Attributional Risk Percent (ARP).
Let’s take cohort study as the first keyword. Start with widely accepted literature. You could start with a search string like “cohort study epidemiology definition”. You could start with Google or Google Scholar.
For illustration purposes, I have selected ERIC Notebook, 2nd edition (Alexander et al., 2014). Let’s take the definition of cohort study from this book.
A cohort study is a type of epidemiological study in which a group of people with a common characteristic is followed over time to find how many reach a certain health outcome of interest (disease,
condition, event, death, or a change in health status or behavior)
Now the most important aspect of writing. You’re not going to copy the exact definition. You need to write it in your own words. Based on given definition, how do you define it?
If you focus on structural definition of a longitudinal nature of cohort studies, you could define it as:
A cohort study is a longitudinal epidemiological design in which a group of individuals sharing a common characteristic (the cohort) is followed over time to observe specific health outcomes, such as a disease or change in health status.
If you want to highlight the risk and incidence measurement aspect of the definition:
A cohort study is an analytic method used to directly calculate risk (cumulative incidence) and incidence rates (incidence density) by quantifying new occurrences of an outcome relative to the population-at-risk or person-time at risk.
Finally, if you want to emphasis the temporal validity (a causal definition) of cohort studies, then you can:
A cohort study design is an observational framework that establishes a clear temporal relationship between cause and effect, as exposure is assessed at baseline while subjects are still free of the outcome.
Now that, you have defined cohort study. You could finally reference the authors of ERIC Notebook as your literature. For this example, I’ll select the second definition.
Following is the APA 7th edition reference of the selected literature.
Alexander, L. K., Lopes, B., Ricchetti-Masterson, K., & Yeatts, K. B. (2014). ERIC Notebook. In ERIC Notebook (2nd edn). UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health. https://sph.unc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/112/2015/07/nciph_ERIC6.pdf
Parenthetical Method
A cohort study is an analytic method used to directly calculate risk (cumulative incidence) and incidence rates (incidence density) by quantifying new occurrences of an outcome relative to the population-at-risk or person-time at risk (Alexander et al., 2014).
Narrative Method
Alexander et al. (2014) define a cohort study as an analytic method used to directly calculate risk (cumulative incidence) and incidence rates (incidence density) by quantifying new occurrences of an outcome relative to the population-at-risk or person-time at risk.
Starting your critical writing with a definition helps you build a good submission with a solid foundation. It also signals the examiner that you’re fully aware of the theory you’re about to discuss. Next, let’s work on the 2×2 table.
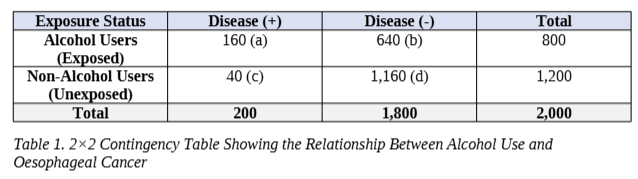
Once you have created the table, make sure to use table caption correctly.
How to handle calculations
In this assignment, you’re asked to calculate RR, AR and ARP. Start with definition, back it up with literature and then write the formula clearly. Then start working on the calculation step by step. Don’t just type in the answer.

After the calculation, make sure to add an interpretation.

Structure of the assignment
Start with a table of contents, then table of figure (if you have used any images or graphs), next table of tables, next table of abbreviations, and finally the name of the assignment.

Use clear headings and subheadings.
Before inserting the references page, add a conclusion. Recap everything in the assignment and provide an overall overview of your answer.
This cohort study demonstrates a strong association between alcohol use and oesophageal cancer. The calculated effect measures show that alcohol users have a six-fold increased risk of developing the disease, with approximately 83.5% of cancer cases among alcohol users attributable to their alcohol consumption. However, the validity of these findings depends on adequate control of confounding factors such as smoking, age, socioeconomic status, and dietary habits. Future studies should employ appropriate methods to address confounding during both the design and analysis stages to provide more reliable estimates of the causal effect of alcohol on oesophageal cancer risk.
Referencing
Use APA 6 or 7.

Finally, here is the complete answer.
Thanks for reading. Please drop your thoughts or feedback.




